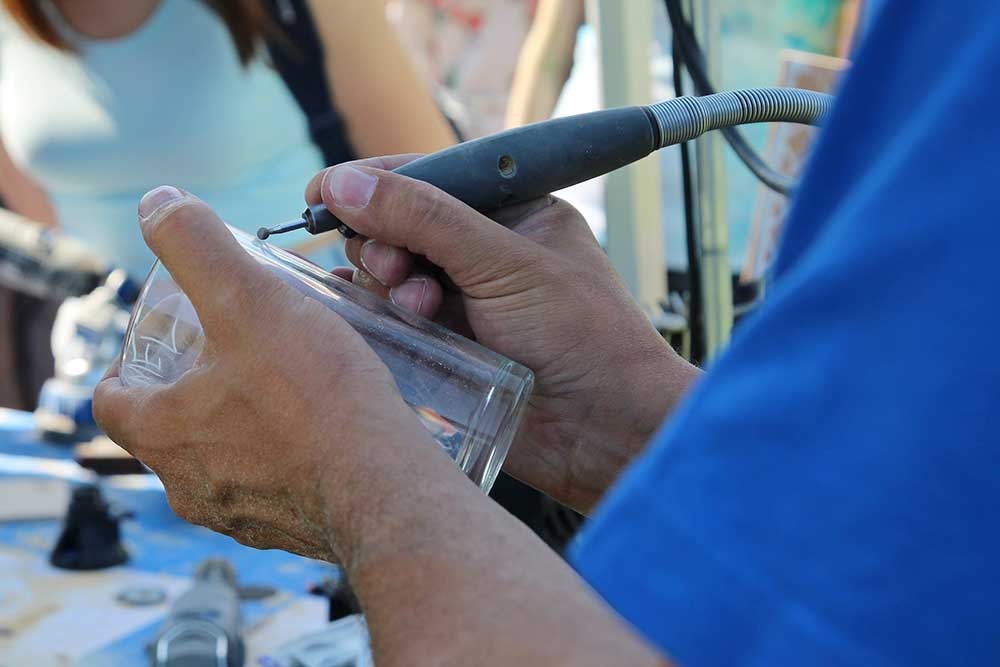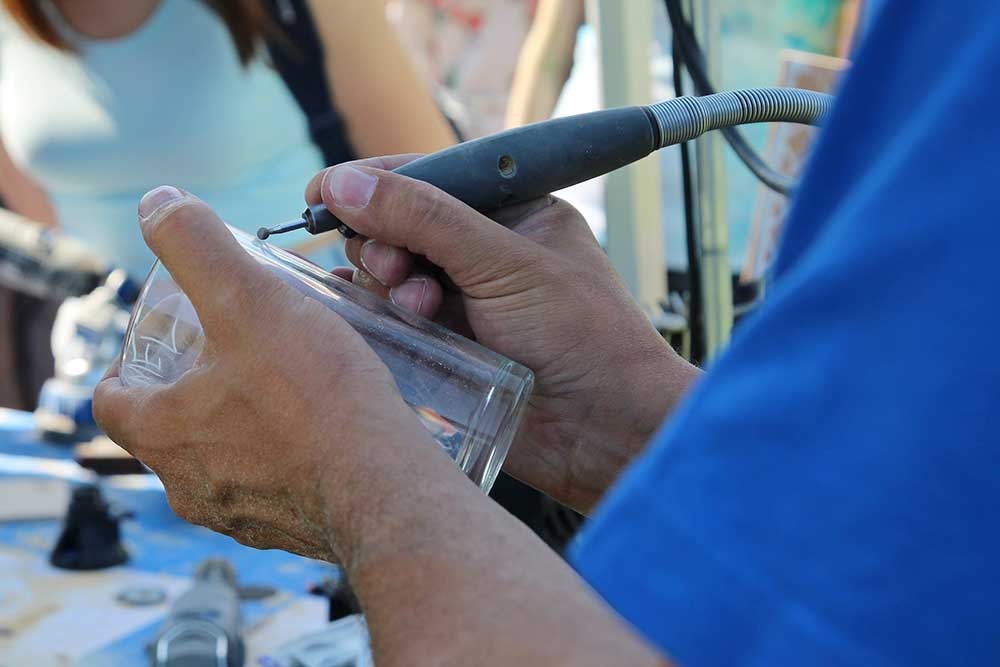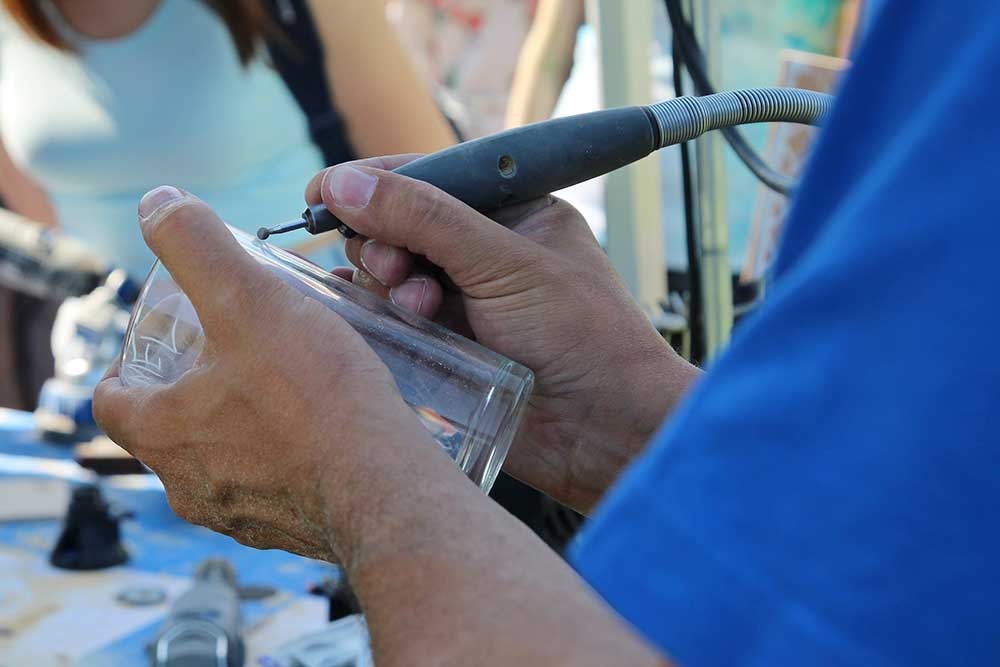- Getting Information — Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
- Controlling Machines and Processes — Using either control mechanisms or direct physical activity to operate machines or processes (not including computers or vehicles).
- Organizing, Planning, and Prioritizing Work — Developing specific goals and plans to prioritize, organize, and accomplish your work.
- Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events — Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
- Handling and Moving Objects — Using hands and arms in handling, installing, positioning, and moving materials, and manipulating things.
- Repairing and Maintaining Mechanical Equipment — Servicing, repairing, adjusting, and testing machines, devices, moving parts, and equipment that operate primarily on the basis of mechanical (not electronic) principles.
- Judging the Qualities of Things, Services, or People — Assessing the value, importance, or quality of things or people.
- Monitor Processes, Materials, or Surroundings — Monitoring and reviewing information from materials, events, or the environment, to detect or assess problems.
- Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates — Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
- Thinking Creatively — Developing, designing, or creating new applications, ideas, relationships, systems, or products, including artistic contributions.
- Making Decisions and Solving Problems — Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
- Interacting With Computers — Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
- Processing Information — Compiling, coding, categorizing, calculating, tabulating, auditing, or verifying information or data.
- Analyzing Data or Information — Identifying the underlying principles, reasons, or facts of information by breaking down information or data into separate parts.
- Evaluating Information to Determine Compliance with Standards — Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards.
- Performing General Physical Activities — Performing physical activities that require considerable use of your arms and legs and moving your whole body, such as climbing, lifting, balancing, walking, stooping, and handling of materials.
- Training and Teaching Others — Identifying the educational needs of others, developing formal educational or training programs or classes, and teaching or instructing others.
- Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge — Keeping up-to-date technically and applying new knowledge to your job.
- Inspecting Equipment, Structures, or Material — Inspecting equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects.
- Estimating the Quantifiable Characteristics of Products, Events, or Information — Estimating sizes, distances, and quantities; or determining time, costs, resources, or materials needed to perform a work activity.
- Scheduling Work and Activities — Scheduling events, programs, and activities, as well as the work of others.
- Documenting/Recording Information — Entering, transcribing, recording, storing, or maintaining information in written or electronic/magnetic form.
- Establishing and Maintaining Interpersonal Relationships — Developing constructive and cooperative working relationships with others, and maintaining them over time.
- Drafting, Laying Out, and Specifying Technical Devices, Parts, and Equipment — Providing documentation, detailed instructions, drawings, or specifications to tell others about how devices, parts, equipment, or structures are to be fabricated, constructed, assembled, modified, maintained, or used.
Read More